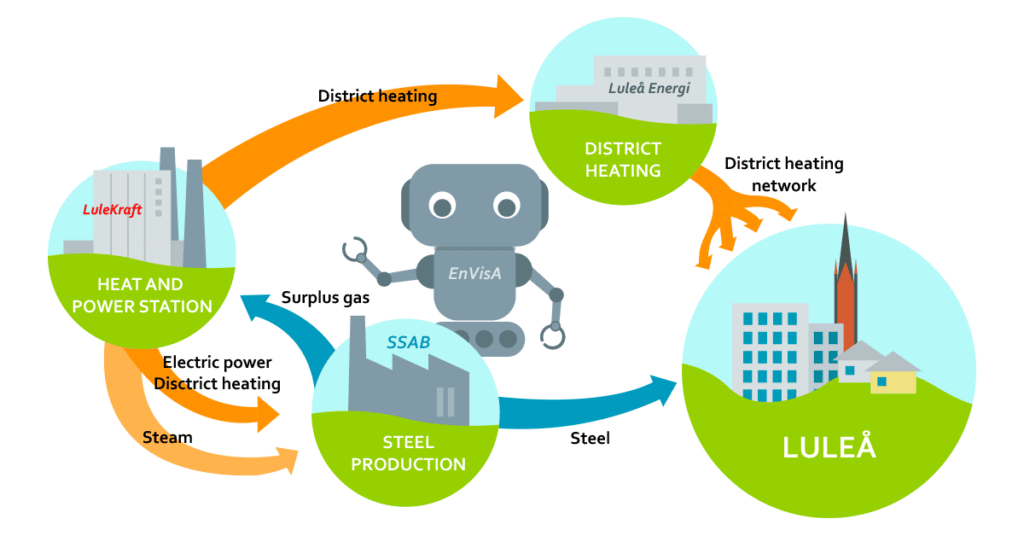
We are developing a new visualization solution with AI prediction as part of the EnVisA (Energy Visualization with Artificial Intelligence) project, which is designed to optimize the use of energy-rich gases produced as a by-product of steel production. EnVisA is a collaboration between Sweden’s leading steel producer, SSAB, energy providers Luleå Energi and LuleKraft, as well as the Swerim Research Institute.
Visualization and AI prediction
Energy-rich gas is produced as a by-product by SSAB and transferred to the LuleKraft powerplant to generate electricity and district heating. The production and consumption of gas must be carefully timed and balanced for optimal usage. If production is momentarily too high, excess gas must be burnt in flares. This loss of gas must then be compensated by burning fossil fuel to meet production targets.
The energy visualization solution will provide a user-friendly real-time view of critical data combined from multiple sources. With shared information readily available, operators will be able to collaborate and make better joint decisions.
To further help the decision-making process, several years of historical data will be analyzed and used to train an AI model. The AI model will make predictions based on current and historical data and identify anomalies and suggest optimal decisions.
The need for green AI
Talking about the project, Data Ductus Senior Machine Learning and Vision Specialist, Martin Simonsson commented, “This is a great example of how we put AI to real use for our partners and clients. Climate change is one of the greatest challenges of our time and as a society we need to come up with solutions that have a real effect. Here at Data Ductus, we are proud to be building AI prediction technology that will help reduce the environmental footprint of not just one but several organizations.”
EnVisA is part of a larger project `AI in the service of climate´ sponsored by Vinnova and Formas, Sweden’s Innovation Agency, and Research Council for Sustainable Development, respectively.
More information about this project can be found here:
https://www.swerim.se/nyheter/okad-ateranvandning-av-energirika-gaser/
https://www.vinnova.se/p/envisa—energivisualisering-med-artificiell-intelligens/
